Advances in Circular RNA Detection Methods Hold Promise for Cancer Diagnostics
December 24th, 2024 8:00 AM
By: Newsworthy Staff
Researchers review progress in molecular diagnostic techniques for circular RNA, highlighting potential applications in cancer biomarkers and disease tracking. The study emphasizes the need for more sensitive and specific detection methods to unlock the full potential of circular RNA in clinical settings.
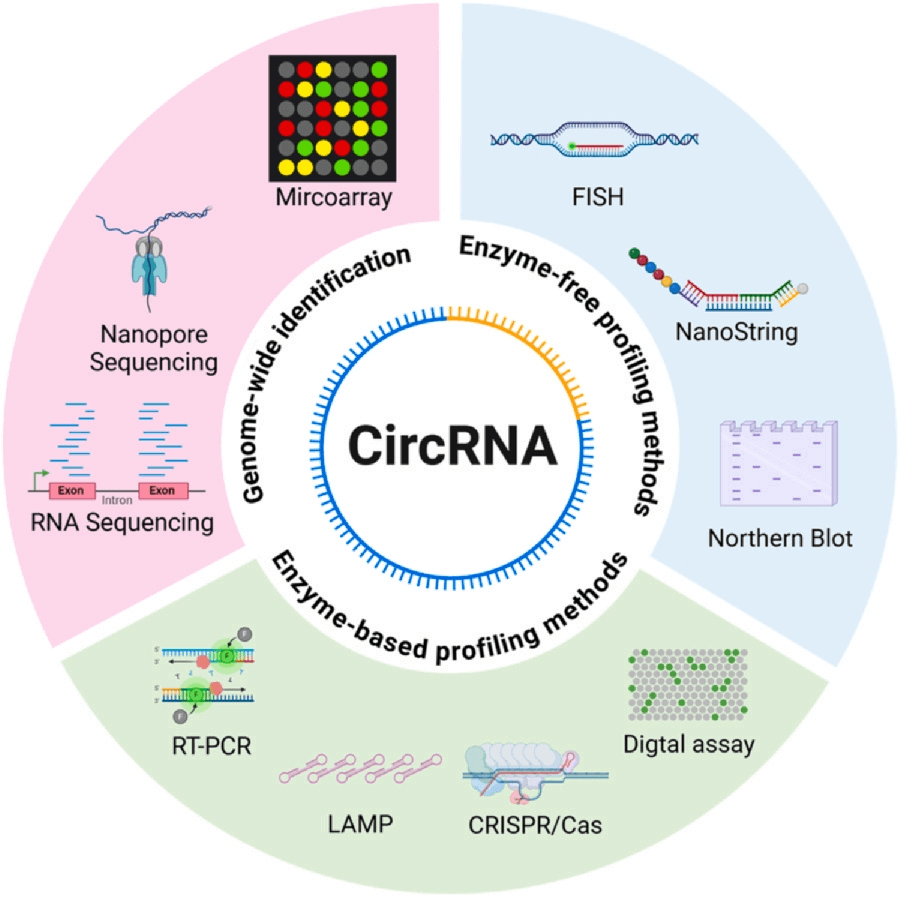
Recent advancements in molecular diagnostic methods for circular RNA (circRNA) are paving the way for improved cancer detection and disease monitoring. A comprehensive review published in the journal Biomedical Analysis outlines the latest developments in circRNA detection technologies, emphasizing their potential as biomarkers for various cancers.
CircRNA, a unique type of non-coding RNA, has gained significant attention in the scientific community since its regulatory functions were discovered in 2013. These molecules, formed by back splicing of mRNA, lack the typical 3'-5' polarity and poly(A) tail found in linear RNA. Their stability and tissue-specific expression patterns make them attractive candidates for biomarkers in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
The study, led by Professor Jiasi Wang from Sun Yat-sen University, highlights the critical role of circRNAs in tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. The researchers note that circRNA expression levels differ substantially between tumors and normal tissues, underlining their potential as cancer biomarkers.
Current detection methods for circRNA, such as RNA sequencing and RT-PCR, have limitations. RNA sequencing, while capable of revealing actual structures and discovering new circRNAs, is expensive, complex, and may miss low-abundance circRNAs. RT-PCR, considered the gold standard for circRNA validation, can overestimate expression due to the molecule's unique circular structure.
The review discusses emerging technologies that aim to address these challenges, including isothermal amplification, CRISPR-based detection, and digital droplet assays. These innovative approaches offer the potential for more sensitive and specific circRNA detection, crucial for understanding their biological functions and tracking disease progression.
Despite significant progress in circRNA research over the past decade, precise detection and quantification, especially in intracellular environments, remain challenging. The circular conformation and sequence overlap with cognate mRNAs pose particular difficulties for researchers.
The implications of this research extend beyond the laboratory. As circRNAs continue to show promise as cancer biomarkers, improved detection methods could lead to earlier and more accurate cancer diagnoses. This, in turn, could result in more effective treatment strategies and better patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the advancement of circRNA detection technologies may accelerate research into other diseases where these molecules play a role, potentially opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions and personalized medicine approaches.
As the field of circRNA research evolves, the development of more precise and efficient detection methods will be crucial. These advancements could not only enhance our understanding of cellular processes but also revolutionize molecular diagnostics in clinical settings, particularly in oncology.
The study underscores the need for continued investment in circRNA research and detection technology development. As these molecular diagnostic methods improve, they may soon become integral tools in clinical laboratories, offering new possibilities for early disease detection, monitoring, and personalized treatment strategies.
Source Statement
This news article relied primarily on a press release disributed by 24-7 Press Release. You can read the source press release here,
